Ruby Quiz
Answer:
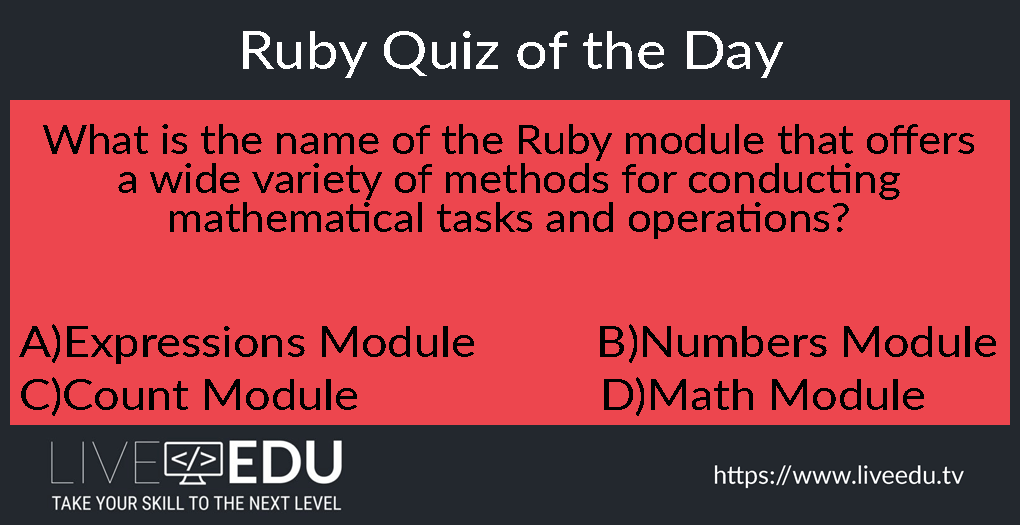
D)
The Ruby Math module provides the Ruby programmer with an extensive range of methods for performing mathematical tasks. In addition, the Math module includes two commonly used mathematical constants:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Math::PI => 3.14159265358979 Math::E => 2.71828182845905 |
As mentioned previously, Ruby provides an extensive range of math related methods. These are listed and described in the following table.
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
| Math.acos, Math.acos! | Arc cosine |
| Math.acosh, Math.acosh! | Hyperbolic arc cosine |
| Math.asin, Math.asin! | Arc sine |
| Math.asinh, Math.asinh | Hyperbolic arc sine |
| Math.atan, Math.atan!, Math.atan2, Math.atan2! | Arc tangent. atan takes an x argument. atan2 takes x and y arguments |
| Math.atanh, Math.atanh! | Hyperbolic arc tangent |
| Math.cos, Math.cos! | Cosine |
| Math.cosh, Math.cosh | Hyperbolic cosine |
| Math.sin, Math.sin! | Sine |
| Math.erf | Error function |
| Match.erfc | Complementary error function |
| Math.exp, Math.exp! | Base x of Euler |
| Math.frexp | Normalized fraction and exponent |
| Math.hypot | Hypotenuse |
| Math.ldexp | Floating-point value corresponding to mantissa and exponent |
| Math.sinh, Math.sinh! | Hyperbolic sine |
| Math.sqrt, Math.sqrt! | Square root |
| Math.tan, Math.tan! | Tangent |
| Math.tanh, Math.tanh! | Hyperbolic tangent |
Now that we have a list of the math methods available to us, we can start to use them:
To perform a square root:
|
1 2 |
Math.sqrt(9) => 3.0 |
Or a Euler calculation:
|
1 2 |
Math.exp(2) => 7.38905609893065 |
If you want to explore more, visit our Ruby edu & tutorials section!
Below are some examples:







